4. CHAPTER 4. STATISTICAL INFERENCE FOR THE MEAN#
SET UP
library(foreign) # to open stata.dta files
library(psych) # for better sammary of descriptive statistics
library(repr) # to combine graphs with adjustable plot dimensions
options(repr.plot.width = 12, repr.plot.height = 6) # Plot dimensions (in inches)
options(width = 150) # To increase character width of printed output
4.1. 4.1 EXAMPLE: MEAN ANNUAL EARNINGS#
df.earn = read.dta(file = "Dataset/AED_EARNINGS.DTA")
print((describe(df.earn)))
vars n mean sd median trimmed mad min max range skew kurtosis se
earnings 1 171 41412.69 25527.05 36000 38052.70 17049.90 1050 172000 170950 1.70 4.23 1952.10
education 2 171 14.43 2.74 14 14.45 2.97 3 20 17 -0.45 1.16 0.21
age 3 171 30.00 0.00 30 30.00 0.00 30 30 0 NaN NaN 0.00
gender 4 171 0.00 0.00 0 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 NaN NaN 0.00
# Summary statisitcs
attach(df.earn)
summary(earnings)
sd(earnings)
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
1050 25000 36000 41413 49000 172000
25527.0533958379
# 95% Confidence interval
t.test(earnings)$"conf.int"
- 37559.20698453
- 45266.1731324291
# Hypothesis test
t.test(earnings, mu=40000)
One Sample t-test
data: earnings
t = 0.72368, df = 170, p-value = 0.4703
alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 40000
95 percent confidence interval:
37559.21 45266.17
sample estimates:
mean of x
41412.69
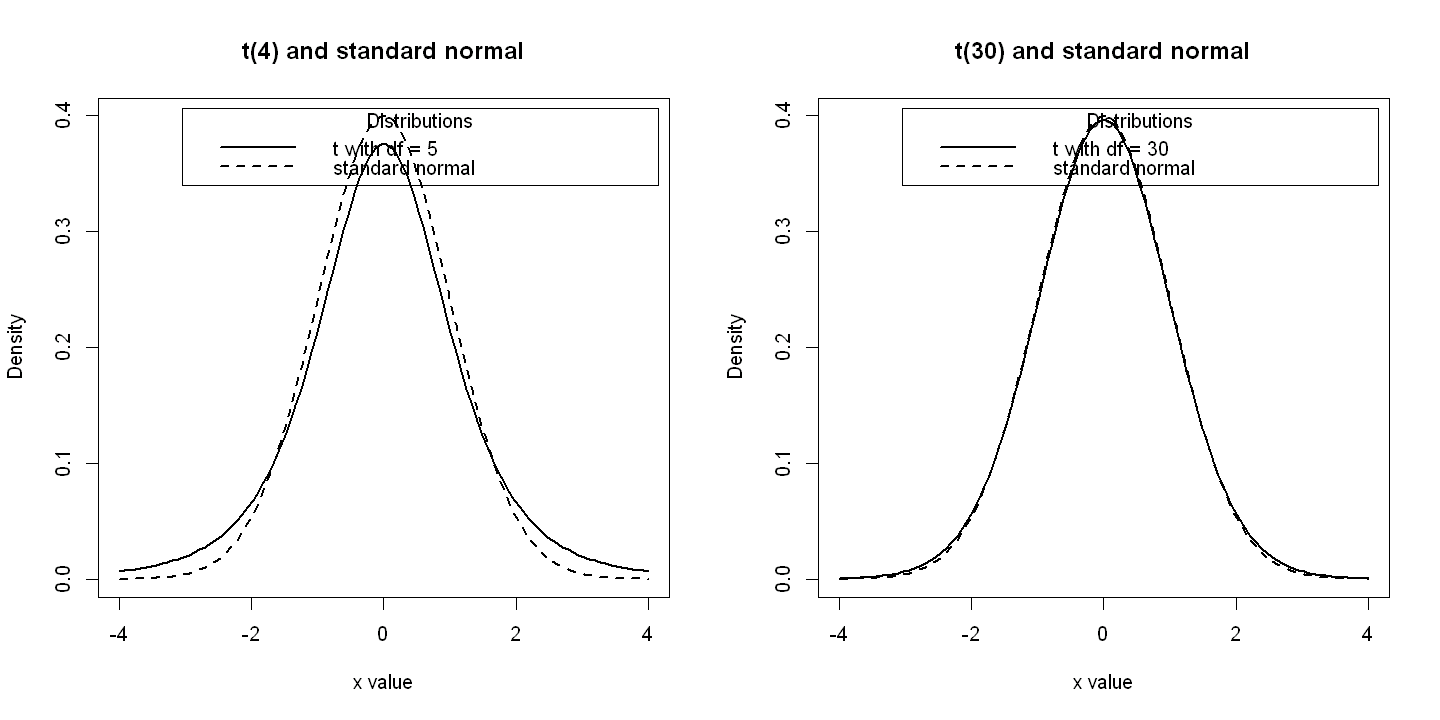
4.2. 4.2 t Statistic and t DISTRIBUTION#
# Plot standard normal and t densities with 4 and 30 degrees of freedom
par(mfrow=c(1,2)) # Combine both panels in one row, two column
# Panel A t(4) and standard normal
x <- seq(-4, 4, length=100)
hx <- dnorm(x)
labels <- c("t with df = 5", "standard normal")
plot(x, hx, type="l", lty=2, lwd=2, xlab="x value",
ylab="Density", main="t(4) and standard normal")
lines(x, dt(x,4), lty=1, lwd=2)
legend("topright", inset=.02, title="Distributions",
labels, lwd=2, lty=c(1, 2))
# Panel B t(30) and standard normal
labels <- c("t with df = 30", "standard normal")
plot(x, hx, type="l", lty=2, lwd=2, xlab="x value",
ylab="Density", main="t(30) and standard normal")
lines(x, dt(x,30), lty=1, lwd=2)
legend("topright", inset=.02, title="Distributions",
labels, lwd=2, lty=c(1, 2))
4.3. 4.3 CONFIDENCE INTERVALS#
summary(earnings)
# 95% Confidence interval
t.test(earnings)$"conf.int"
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
1050 25000 36000 41413 49000 172000
- 37559.20698453
- 45266.1731324291
# 90% and 99% confidence intervals
t.test(earnings, conf.level=0.90)$"conf.int"
t.test(earnings, conf.level=0.99)$"conf.int"
- 38184.1733816741
- 44641.206735285
- 36327.3489591822
- 46498.0311577768
# Confidence interval manually
mean = mean(earnings)
sd = sd(earnings)
N = length(earnings)
sterror = sd/sqrt(N)
tcrit = qt(.975,N-1)
intwidth = tcrit*sterror
print("95% confidence interval = ")
cbind(mean - intwidth, mean + intwidth)
[1] "95% confidence interval = "
| 37559.21 | 45266.17 |
4.4. 4.4 TWO-SIDED HYPOTHESIS TEST#
# Test H0: mu = 40000 against HA: mu not = 40000
t.test(earnings, mu = 40000)
One Sample t-test
data: earnings
t = 0.72368, df = 170, p-value = 0.4703
alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 40000
95 percent confidence interval:
37559.21 45266.17
sample estimates:
mean of x
41412.69
# Same two-sided test done manually
mu0 = 40000
mean = mean(earnings)
sd = sd(earnings)
N = length(earnings)
sterror = sd/sqrt(N)
t = (mean-mu0)/sterror
p = 2*(1-pt(abs(t),N-1))
# Equivalent is 2*pt(t,N-1,lower.tail=FALSE)
tcrit = qt(.975,N-1)
print("t statistic, p-value, critical value")
cbind(t, p, tcrit)
[1] "t statistic, p-value, critical value"
| t | p | tcrit |
|---|---|---|
| 0.7236761 | 0.4702592 | 1.974017 |
4.5. 4.5 TWO-SIDED HYPOTHESIS TEST EXAMPLES#
# Gasoline price September 2 2013 from sactogasprices.com part of GasBuddy.com
rm(list=ls())
library(foreign)
df = read.dta(file = "Dataset/AED_GASPRICE.DTA")
attach(df)
print((describe(df)))
summary(price)
vars n mean sd median trimmed mad min max range skew kurtosis se
city* 1 32 1.91 0.73 2.00 1.88 1.48 1.00 3.00 2.0 0.14 -1.20 0.13
price 2 32 3.67 0.15 3.65 3.65 0.18 3.49 4.09 0.6 0.71 0.14 0.03
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
3.49 3.55 3.65 3.67 3.79 4.09
# Test H0: mu = 3.81 against HA: mu not = 50000
t.test(price, mu = 3.81)
t = (3.6697-3.81)/(0.1510/sqrt(32))
p = 2*(1-pt(abs(t),31))
tcrit = qt(.975,31)
cbind(t, p, tcrit)
One Sample t-test
data: price
t = -5.2577, df = 31, p-value = 1.026e-05
alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 3.81
95 percent confidence interval:
3.615259 3.724116
sample estimates:
mean of x
3.669687
| t | p | tcrit |
|---|---|---|
| -5.256004 | 1.03076e-05 | 2.039513 |
# Male Earnings 2010 30 year old full time workers
df = read.dta(file = "Dataset/AED_EARNINGSMALE.DTA")
attach(df)
print((describe(df)))
summary(earnings)
The following objects are masked from df.earn:
age, earnings, education, gender
vars n mean sd median trimmed mad min max range skew kurtosis se
earnings 1 191 52353.93 65034.74 38000 41328.76 20756.40 1 498000 497999 5.31 32.38 4705.75
education 2 191 13.43 3.01 13 13.55 1.48 0 20 20 -1.12 3.95 0.22
age 3 191 30.00 0.00 30 30.00 0.00 30 30 0 NaN NaN 0.00
gender 4 191 1.00 0.00 1 1.00 0.00 1 1 0 NaN NaN 0.00
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
1 25500 38000 52354 58850 498000
# Test H0: mu = 50000 against HA: mu not = 50000
t.test(earnings, mu=50000)
t = (52353.93-50000)/(65034.74/sqrt(191))
p = 2*(1-pt(abs(t),190))
tcrit= qt(.975,190)
cbind(t, p, tcrit)
One Sample t-test
data: earnings
t = 0.50022, df = 190, p-value = 0.6175
alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 50000
95 percent confidence interval:
43071.71 61636.15
sample estimates:
mean of x
52353.93
| t | p | tcrit |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5002243 | 0.617496 | 1.972528 |
# Growth in real GDP per capita
# Read in the Stata data set - requires package foreign
df = read.dta(file = "Dataset/AED_REALGDPPC.DTA")
attach(df)
print((describe(df)))
summary(growth)
Warning message in FUN(newX[, i], ...):
"no non-missing arguments to min; returning Inf"
Warning message in FUN(newX[, i], ...):
"no non-missing arguments to max; returning -Inf"
vars n mean sd median trimmed mad min max range skew kurtosis se
gdpc1 1 245 9925.24 4814.02 9238.92 9716.91 6140.55 3121.94 19221.97 16100.03 0.32 -1.25 307.56
gdp 2 245 7401.46 6331.00 5695.36 6755.00 6885.44 510.33 21729.12 21218.79 0.65 -0.88 404.47
gdpdef 3 245 59.72 31.20 61.65 59.06 44.57 16.35 113.50 97.16 0.03 -1.36 1.99
date* 4 245 123.00 70.87 123.00 123.00 90.44 1.00 245.00 244.00 0.00 -1.21 4.53
daten 5 245 NaN NA NA NaN NA Inf -Inf -Inf NA NA NA
quarter 6 245 118.00 70.87 118.00 118.00 90.44 -4.00 240.00 244.00 0.00 -1.21 4.53
popthm 7 245 253116.88 45611.79 247695.00 252742.75 58854.77 176044.00 329527.00 153483.00 0.10 -1.28 2914.03
year 8 245 1989.13 17.72 1989.00 1989.13 22.24 1959.00 2020.00 61.00 0.00 -1.21 1.13
realgdp 9 245 9925.24 4814.03 9238.97 9716.90 6140.78 3121.86 19222.00 16100.14 0.32 -1.25 307.56
gdppc 10 245 25841.47 19184.69 22993.15 24423.21 24740.38 2898.86 66008.59 63109.73 0.44 -1.13 1225.66
realgdppc 11 245 37050.50 12089.68 36929.01 36996.63 16507.15 17733.26 58392.45 40659.20 0.08 -1.33 772.38
growth 12 241 1.99 2.18 2.09 2.08 1.80 -4.77 7.63 12.40 -0.38 0.64 0.14
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max. NA's
-4.7722 0.8924 2.0896 1.9905 3.3142 7.6305 4
# Test H0: mu = 2.0 against HA: mu not = 2.0
t.test(growth, mu=2.0)
t = (1.9904-2.0)/(2.1781/sqrt(241))
p = 2*(1-pt(abs(t),241))
tcrit= qt(.975,241)
cbind(t, p, tcrit)
One Sample t-test
data: growth
t = -0.068021, df = 240, p-value = 0.9458
alternative hypothesis: true mean is not equal to 2
95 percent confidence interval:
1.714073 2.266840
sample estimates:
mean of x
1.990456
| t | p | tcrit |
|---|---|---|
| -0.06842297 | 0.9455057 | 1.969856 |
4.6. 4.6 ONE-SIDED DIRECTIONAL HYPOTHESIS TESTS#
t.test(earnings, mu=50000, alternative = "less")
One Sample t-test
data: earnings
t = 0.50022, df = 190, p-value = 0.6913
alternative hypothesis: true mean is less than 50000
95 percent confidence interval:
-Inf 60132.12
sample estimates:
mean of x
52353.93
df.earn = read.dta(file = "Dataset/AED_EARNINGS.DTA")
attach(df.earn)
print((describe(df.earn)))
summary(earnings)
The following objects are masked from df (pos = 4):
age, earnings, education, gender
The following objects are masked from df.earn (pos = 6):
age, earnings, education, gender
vars n mean sd median trimmed mad min max range skew kurtosis se
earnings 1 171 41412.69 25527.05 36000 38052.70 17049.90 1050 172000 170950 1.70 4.23 1952.10
education 2 171 14.43 2.74 14 14.45 2.97 3 20 17 -0.45 1.16 0.21
age 3 171 30.00 0.00 30 30.00 0.00 30 30 0 NaN NaN 0.00
gender 4 171 0.00 0.00 0 0.00 0.00 0 0 0 NaN NaN 0.00
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
1050 25000 36000 41413 49000 172000
# Test H0: mu < 40000 against HA: mu >= 40000 using Stata command ttest
t.test(earnings, mu=40000, alternative = "greater")
One Sample t-test
data: earnings
t = 0.72368, df = 170, p-value = 0.2351
alternative hypothesis: true mean is greater than 40000
95 percent confidence interval:
38184.17 Inf
sample estimates:
mean of x
41412.69
# Same two-sided test done manually
mu0 = 40000
mean = mean(earnings)
sd = sd(earnings)
N = length(earnings)
sterror = sd/sqrt(N)
t = (mean-mu0)/sterror
p = 1-pt(abs(t),N-1)
# Equivalent is pt(t,N-1,lower.tail=FALSE)
tcrit = qt(.95,N-1)
print("t statistic, p-value, critical value")
cbind(t, p, tcrit)
[1] "t statistic, p-value, critical value"
| t | p | tcrit |
|---|---|---|
| 0.7236761 | 0.2351296 | 1.653866 |
4.7. 4.8 PROPORTIONS DATA#
# Confidence interval
mean = (480*1+441*0)/921
sterror = sqrt( (mean*(1-mean)) / 921)
print("mean and standard error")
cbind(mean, sterror)
print("95% CI")
cbind(mean-1.964*sterror, mean+1.964*sterror)
[1] "mean and standard error"
| mean | sterror |
|---|---|
| 0.5211726 | 0.01646078 |
[1] "95% CI"
| 0.4888437 | 0.5535016 |
# Test mu = 0.50
sterrorH0 = sqrt( (0.5*(1-0.5)) / 921)
t = (mean - 0.5) / sterrorH0
p = 2*(1-pnorm(abs(t)))
print("t statistic, p-value, critical value")
cbind(t, p, tcrit)
[1] "t statistic, p-value, critical value"
| t | p | tcrit |
|---|---|---|
| 1.285094 | 0.1987595 | 1.653866 |